
The exact pattern you get depends on which measure of atomic radius you use - but the trends are still valid. Trends in atomic radius in the Periodic Table Note: If you want to explore these various types of bonding this link will take you to the bonding menu. This measure of atomic radius is called the van der Waals radius after the weak attractions present in this situation. The attractive forces are much less, and the atoms are essentially "unsquashed". The right hand diagram shows what happens if the atoms are just touching. The type of atomic radius being measured here is called the metallic radius or the covalent radius depending on the bonding. This is what you would get if you had metal atoms in a metallic structure, or atoms covalently bonded to each other.
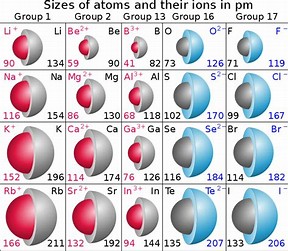
The atoms are pulled closely together and so the measured radius is less than if they are just touching. The left hand diagram shows bonded atoms. The radius of an atom can only be found by measuring the distance between the nuclei of two touching atoms, and then halving that distance.Īs you can see from the diagrams, the same atom could be found to have a different radius depending on what was around it. Unlike a ball, an atom doesn't have a fixed radius. Important! If you aren't reasonable happy about electronic structures you should follow this link before you go any further.

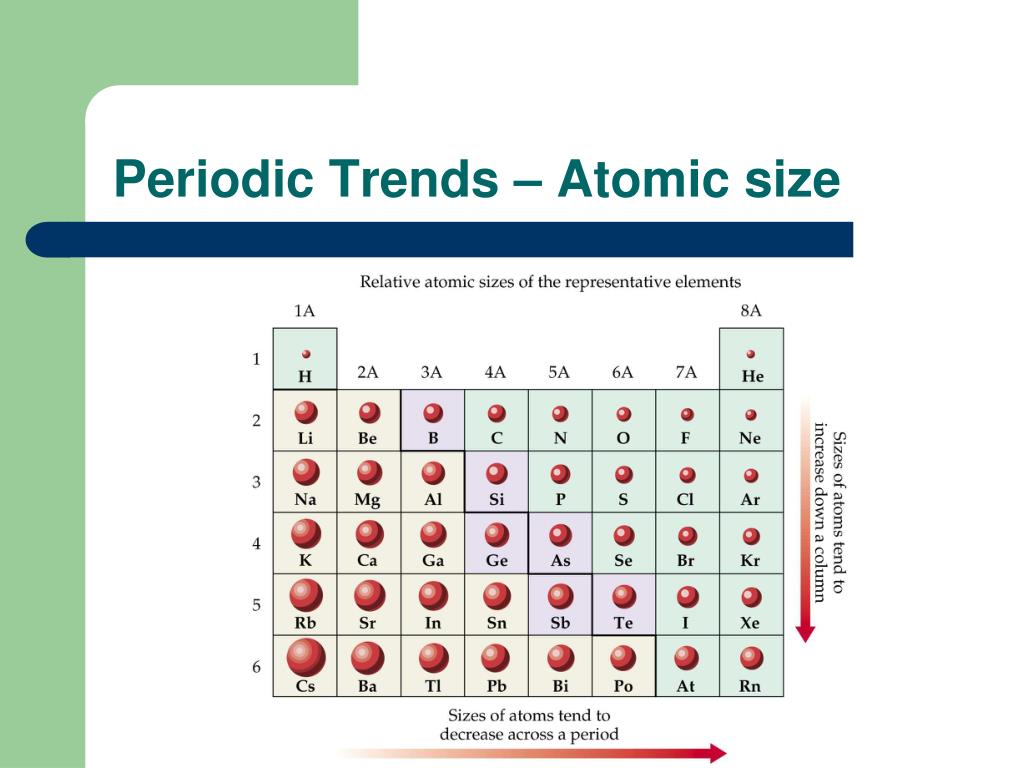
It assumes that you understand electronic structures for simple atoms written in s, p, d notation. This page explains the various measures of atomic radius, and then looks at the way it varies around the Periodic Table - across periods and down groups.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
